Technology application
Popularization of Science| Parallel Seam Welding of Airtight Packaging Basis Ⅰ
Release time
2024-05-28
The airtight packaging of microelectronic devices is mainly divided into parallel seam welding, energy storage sealing, laser sealing and vacuum eutectic reflow oven for AuSn melting sealing. Parallel seam welding is mainly used in ceramic base, which is a kind of airtight packaging form with the most application scenarios.
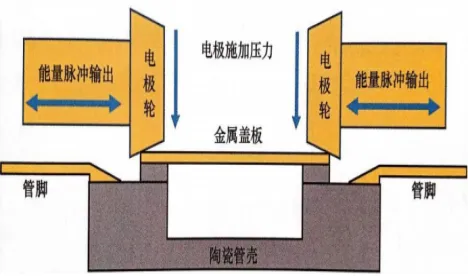
The principle of parallel seam welding is mainly that two conical electrodes are in contact with the cover plate to provide a closed loop for the current. When the two electrodes roll along the edge of the metal cover plate, a series of short high-frequency power pulses between the two electrodes generate extremely high local heat at the contact point between the electrode and the cover plate melts and forms a continuous and complete seal welding area.
That is Q=I²*R*T. (I is current; R is resistance; t is time).
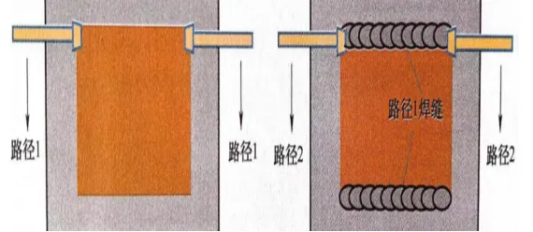
Parallel seam welding is generally performed in a nitrogen environment. The nitrogen environment is provided by an air-tight glove box. The glove box consists of an oven, a nitrogen box, an antechamber, a vacuum pump, a nitrogen purification system, a water analyzer, and an oxygen analyzer. According to the process requirements, baking time, temperature, vacuum degree and other parameters can be set in the program. The water and oxygen analyzer are used to detect the water and oxygen content in the box, thus providing a standard environment for seam welding. Equipped with a nitrogen in the box can automatically enter the purification system, and then enter the box after water and oxygen removal. It can quickly reach the water and oxygen content required for seam welding, and save the amount of nitrogen. The specific process of parallel seam welding is shown in the following figure:

Parallel seam welding, as the most widely used form of airtight packaging, has the following advantages:
- The method of local heating has little impact on the chip and low cost.
- It is necessary to vacuum bake the device before seam welding, which can reduce the water and oxygen content in the base chamber and control the internal atmosphere of the chamber.
- The seam welding process is filled with inert gas, and its pressure is similar to atmospheric pressure. And the balance of internal and external pressure during the use of the device can work for a long time.
- The seam welding process is basically automatic control. With less manual intervention, the packaging process is more stable and the yield is higher.

At same time, there are some shortcomings:
- When the flat seam is fused, the surface coating of the base cover melts, and the coating structure is destroyed, which will lead to the deterioration of the salt spray resistance.
- Flat seam can only be welded to rectangular, circular and other regular bases, and the cover surface is required to be on the same plane.
- In the process of flat seam welding, if the process parameters are not adjusted properly and the input energy is too large, it is easy to cause heat accumulation on the base and lead to overheating of the device. (It may cause cracking at glass insulator for metal bases. For ceramic bases, this may cause delamination and cracking.) The weld temperature of parallel seam welding is high, but the temperature rise of the main body of the base is low, and there is usually a large temperature gradient in the joint part of the welding ring and the ceramic, which will produce a certain degree of thermal stress.
- The loading and unloading of parallel seam welding is manually operated, and the cover plate alignment deviation or contamination may occur. The large alignment deviation will cause the surface weld to be corrode by fire during welding or the solder to be missing in the sealing area. Welding surface contamination is easy to form pores and other defects.
There are many forms of airtight packaging, which need to be selected according to the combination of base material, cover plate material, solder composition, the shape and thickness of base, and aging screening requirements, etc.
(To be continued…)
Previous Page


